Hcf Of 30 And 105
dulhadulhi
Sep 10, 2025 · 5 min read
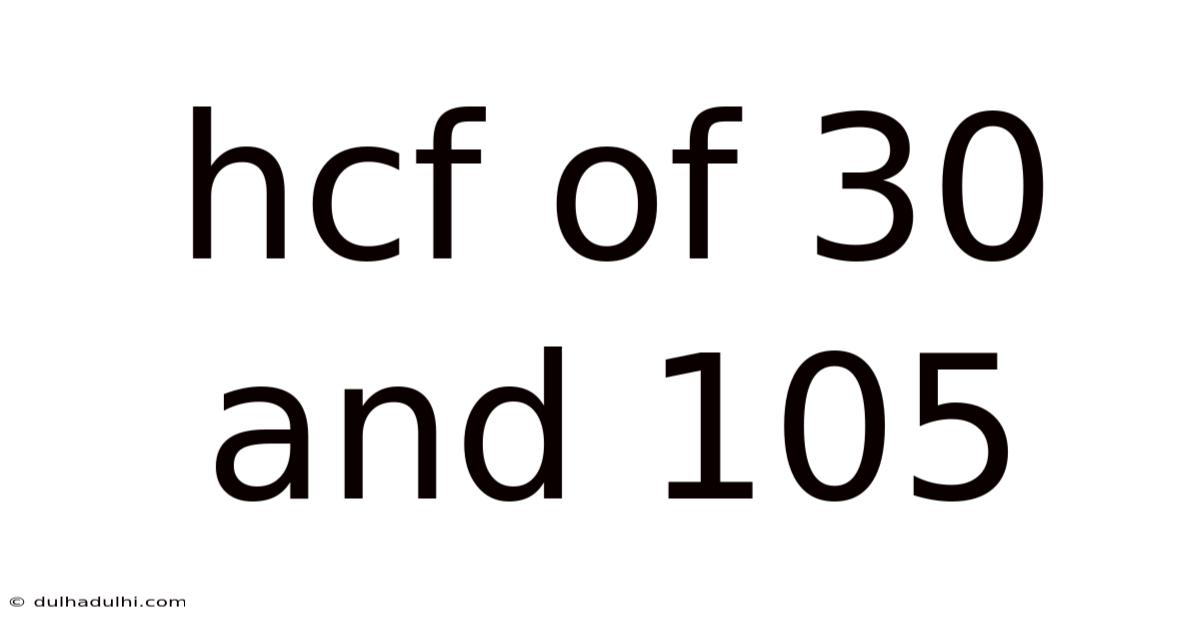
Table of Contents
Finding the Highest Common Factor (HCF) of 30 and 105: A Comprehensive Guide
Finding the highest common factor (HCF), also known as the greatest common divisor (GCD), of two numbers is a fundamental concept in mathematics. This article will delve into the process of calculating the HCF of 30 and 105, exploring various methods and providing a deeper understanding of the underlying principles. We'll cover prime factorization, the Euclidean algorithm, and other techniques, equipping you with the knowledge to tackle similar problems with confidence. Understanding HCF is crucial for simplifying fractions, solving algebraic equations, and comprehending more advanced mathematical concepts.
Introduction to Highest Common Factor (HCF)
The highest common factor (HCF) of two or more numbers is the largest number that divides each of the numbers without leaving a remainder. In simpler terms, it's the biggest number that goes into both numbers evenly. For example, the HCF of 12 and 18 is 6 because 6 is the largest number that divides both 12 and 18 without leaving any remainder. This concept is important in various areas of mathematics and its applications in real-world scenarios.
Method 1: Prime Factorization
This method involves breaking down each number into its prime factors—numbers divisible only by 1 and themselves. The HCF is then found by identifying the common prime factors and multiplying them together.
Let's apply this method to find the HCF of 30 and 105:
1. Prime Factorization of 30:
30 can be broken down as follows:
- 30 = 2 × 15
- 15 = 3 × 5
Therefore, the prime factorization of 30 is 2 × 3 × 5.
2. Prime Factorization of 105:
105 can be broken down as follows:
- 105 = 3 × 35
- 35 = 5 × 7
Therefore, the prime factorization of 105 is 3 × 5 × 7.
3. Identifying Common Factors:
Comparing the prime factorizations of 30 (2 × 3 × 5) and 105 (3 × 5 × 7), we see that the common prime factors are 3 and 5.
4. Calculating the HCF:
Multiplying the common prime factors together, we get:
HCF(30, 105) = 3 × 5 = 15
Therefore, the highest common factor of 30 and 105 is 15.
Method 2: The Euclidean Algorithm
The Euclidean algorithm is an efficient method for finding the HCF of two numbers, especially when dealing with larger numbers. It's based on the principle that the HCF of two numbers does not change if the larger number is replaced by its difference with the smaller number. This process is repeated until the two numbers are equal, and that number is the HCF.
Let's apply the Euclidean algorithm to find the HCF of 30 and 105:
1. Initial Step:
We start with the two numbers: 30 and 105. Since 105 is larger, we'll subtract 30 from 105 repeatedly until we get a number less than 30.
105 - 30 = 75 75 - 30 = 45 45 - 30 = 15
Now we have 15 and 30.
2. Repeated Subtraction:
Now we repeat the process with 15 and 30:
30 - 15 = 15
Now we have 15 and 15.
3. Result:
Since both numbers are now equal to 15, the HCF of 30 and 105 is 15.
Method 3: Listing Factors
This is a more straightforward method, suitable for smaller numbers. It involves listing all the factors of each number and identifying the largest common factor.
1. Factors of 30: 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 10, 15, 30
2. Factors of 105: 1, 3, 5, 7, 15, 21, 35, 105
3. Common Factors: Comparing the lists, the common factors are 1, 3, 5, and 15.
4. Highest Common Factor: The largest common factor is 15. Therefore, the HCF of 30 and 105 is 15.
Understanding the Significance of HCF
The HCF has several significant applications in mathematics and beyond:
-
Simplifying Fractions: The HCF is crucial for simplifying fractions to their lowest terms. For instance, the fraction 30/105 can be simplified by dividing both the numerator and the denominator by their HCF, which is 15, resulting in the simplified fraction 2/7.
-
Solving Algebraic Equations: HCF is often used in solving algebraic equations involving fractions and factoring expressions. Finding the HCF of coefficients can help simplify equations and make them easier to solve.
-
Geometry and Measurement: HCF finds application in solving geometric problems related to area, volume, and finding the greatest common length that can measure two given lengths without leaving a remainder.
-
Number Theory: HCF forms the basis of many concepts in number theory, including modular arithmetic and the study of prime numbers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What if the HCF of two numbers is 1?
A1: If the HCF of two numbers is 1, it means the numbers are relatively prime or coprime. This implies that they share no common factors other than 1.
Q2: Can the HCF of two numbers be larger than the smaller number?
A2: No, the HCF can never be larger than the smaller of the two numbers. By definition, the HCF must divide both numbers without leaving a remainder.
Q3: Is there a difference between HCF and GCD?
A3: No, HCF (Highest Common Factor) and GCD (Greatest Common Divisor) are two different names for the same concept. They both represent the largest number that divides both given numbers without any remainder.
Q4: How can I find the HCF of more than two numbers?
A4: To find the HCF of more than two numbers, you can extend the methods described above. For prime factorization, find the prime factorization of each number and then identify the common prime factors with the lowest power. For the Euclidean algorithm, you can find the HCF of two numbers first and then find the HCF of the result and the next number, repeating the process until all numbers are considered.
Conclusion
Finding the highest common factor (HCF) of 30 and 105, as demonstrated through prime factorization and the Euclidean algorithm, reveals the fundamental importance of this mathematical concept. Understanding different methods for calculating the HCF empowers you to approach various mathematical problems efficiently. From simplifying fractions to solving complex equations, the HCF plays a crucial role in various mathematical operations and real-world applications. Remember to choose the method that best suits the numbers involved and your level of comfort with different mathematical approaches. The understanding of HCF allows for a more profound appreciation of the interconnectedness and elegance within mathematics. It's a cornerstone concept that continues to be essential in both theoretical and practical contexts.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Hcf Of 30 And 105 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.