1 4 Divided By 2
dulhadulhi
Sep 24, 2025 · 5 min read
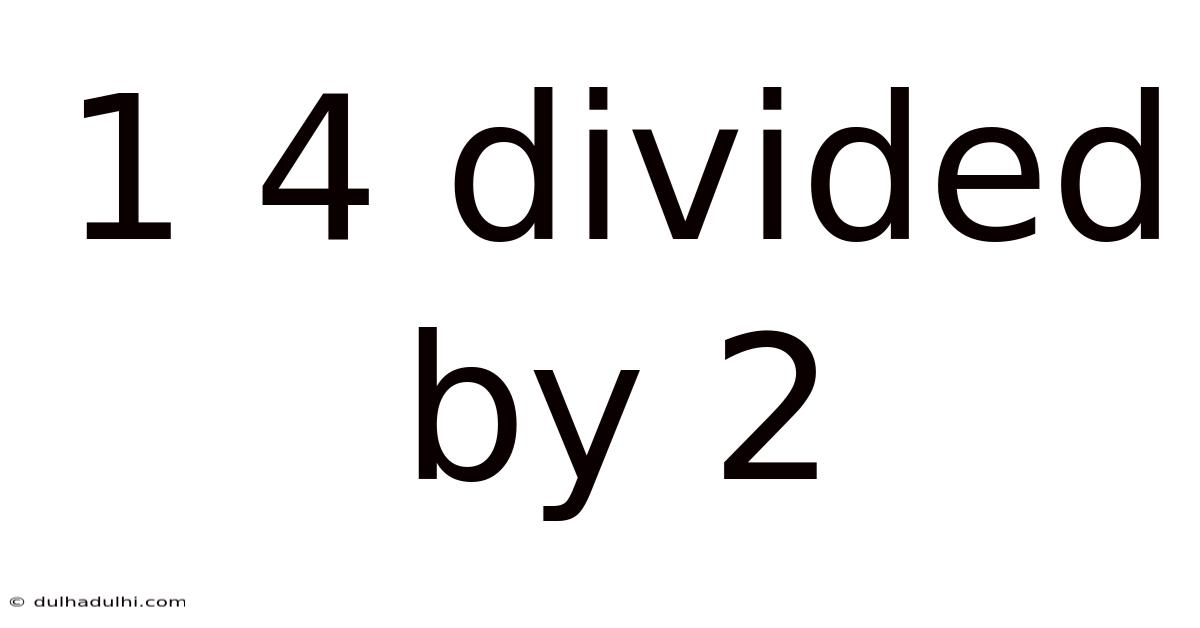
Table of Contents
14 Divided by 2: A Deep Dive into Simple Division and its Broader Applications
This article explores the seemingly simple mathematical operation of 14 divided by 2, delving beyond the immediate answer to uncover the underlying principles of division, its various applications, and its significance in broader mathematical contexts. We'll examine different methods of solving this problem, discuss the concepts of dividends, divisors, quotients, and remainders, and touch upon the role of division in more complex mathematical operations. Understanding this fundamental operation forms a crucial cornerstone for grasping more advanced mathematical concepts.
Introduction: The Fundamentals of Division
Division is one of the four basic arithmetic operations, alongside addition, subtraction, and multiplication. It essentially represents the process of splitting a quantity into equal parts or groups. In the case of 14 divided by 2 (often written as 14 ÷ 2, 14/2, or 2)14), we are asking: "How many times does 2 fit into 14?" The immediate and straightforward answer is 7. However, this simple equation opens a door to a deeper understanding of mathematical principles.
Methods for Solving 14 Divided by 2
While the answer to 14 ÷ 2 is readily apparent, exploring different approaches to solving this problem reinforces fundamental mathematical concepts.
-
Repeated Subtraction: This method involves repeatedly subtracting the divisor (2) from the dividend (14) until the remainder is zero. Each subtraction represents one group of 2.
14 - 2 = 12 12 - 2 = 10 10 - 2 = 8 8 - 2 = 6 6 - 2 = 4 4 - 2 = 2 2 - 2 = 0
We subtracted 2 seven times, therefore, 14 ÷ 2 = 7.
-
Long Division: This formal method is particularly useful for more complex division problems. Although seemingly unnecessary for 14 ÷ 2, applying the long division algorithm helps solidify the process for more challenging divisions.
7 2|14 14 -- 0We divide 14 by 2, resulting in a quotient of 7 and a remainder of 0.
-
Multiplication: Division and multiplication are inverse operations. To solve 14 ÷ 2, we can ask: "What number, when multiplied by 2, equals 14?" The answer, of course, is 7 (2 x 7 = 14).
Understanding Key Terms: Dividend, Divisor, Quotient, and Remainder
Understanding the terminology associated with division is crucial. In the equation 14 ÷ 2 = 7:
- Dividend: This is the number being divided (14).
- Divisor: This is the number by which the dividend is divided (2).
- Quotient: This is the result of the division (7). It represents the number of times the divisor goes into the dividend.
- Remainder: This is the amount left over after dividing. In this case, the remainder is 0, indicating that the division is exact.
Division with Remainders: Moving Beyond Exact Divisions
While 14 ÷ 2 results in a clean quotient, many division problems produce remainders. For example, if we divide 15 by 2:
15 ÷ 2 = 7 with a remainder of 1.
This means 2 goes into 15 seven times, with 1 left over. Understanding remainders is essential in various applications, such as sharing items equally or dealing with fractional parts.
Real-World Applications of Division: Everyday Examples
Division is far from an abstract mathematical concept; it's a fundamental tool used in countless everyday situations. Here are a few examples:
- Sharing: Dividing a pizza among friends involves division. If you have 14 slices and 2 friends, each friend gets 7 slices (14 ÷ 2 = 7).
- Measurement: Calculating the number of 2-meter lengths needed to cover a 14-meter distance involves division (14 ÷ 2 = 7 lengths).
- Rate and Ratio: Determining the average speed involves division. If you travel 14 kilometers in 2 hours, your average speed is 7 kilometers per hour (14 ÷ 2 = 7).
- Financial Calculations: Dividing your total expenses by the number of months determines your average monthly spending.
- Recipe Scaling: Adjusting a recipe to serve more or fewer people often requires division. If a recipe calls for 2 cups of flour and you want to double it, you'll need 4 cups (2 x 2 = 4). Conversely, halving a recipe might involve dividing ingredient quantities by 2.
Division in Advanced Mathematics: Expanding the Scope
The simple operation of 14 ÷ 2 serves as a foundation for more complex mathematical concepts:
- Fractions: Division is intrinsically linked to fractions. 14 ÷ 2 can be represented as the fraction 14/2, which simplifies to 7. Fractions represent parts of a whole and are crucial in various mathematical fields.
- Algebra: Division is used extensively in algebraic manipulations to solve equations and simplify expressions. For example, solving the equation 2x = 14 requires dividing both sides by 2 to find x = 7.
- Calculus: Division plays a crucial role in calculus, particularly in differentiation and integration.
- Statistics: Division is involved in calculating averages, standard deviations, and other statistical measures.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- What is the inverse operation of division? Multiplication is the inverse operation of division.
- Can you divide by zero? No, division by zero is undefined in mathematics. It leads to indeterminate results.
- What if the dividend is smaller than the divisor? If the dividend is smaller than the divisor, the quotient is 0, and the remainder is equal to the dividend. For example, 1 ÷ 2 = 0 with a remainder of 1.
- How do I handle decimals in division? The principles of division remain the same when dealing with decimals. However, the process might involve more steps and potentially lead to repeating decimals.
- Are there different notations for division? Yes, division can be represented in several ways: 14 ÷ 2, 14/2, 2)14.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Division
The seemingly simple calculation of 14 divided by 2 reveals a rich tapestry of mathematical concepts and practical applications. From the fundamental operations of repeated subtraction and long division to its crucial role in fractions, algebra, and advanced mathematics, division is a cornerstone of mathematical understanding. Mastering division is not merely about finding the answer to a specific problem; it's about developing a deeper appreciation for the logic and structure underpinning the world of numbers and their applications in our daily lives. It’s a building block upon which more complex mathematical skills are constructed, paving the way for further exploration and discovery within the fascinating realm of mathematics. The seemingly simple act of dividing 14 by 2 underscores the power and elegance of even the most fundamental mathematical principles.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Litres To Gallons Calculator Uk
Sep 24, 2025
-
Metals That Are Not Magnetic
Sep 24, 2025
-
How To Get Horny Fast
Sep 24, 2025
-
Blood Test For Blood Type
Sep 24, 2025
-
Prime Factor Tree For 30
Sep 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 1 4 Divided By 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.